Understanding the Challenge of Autoimmune Disorders
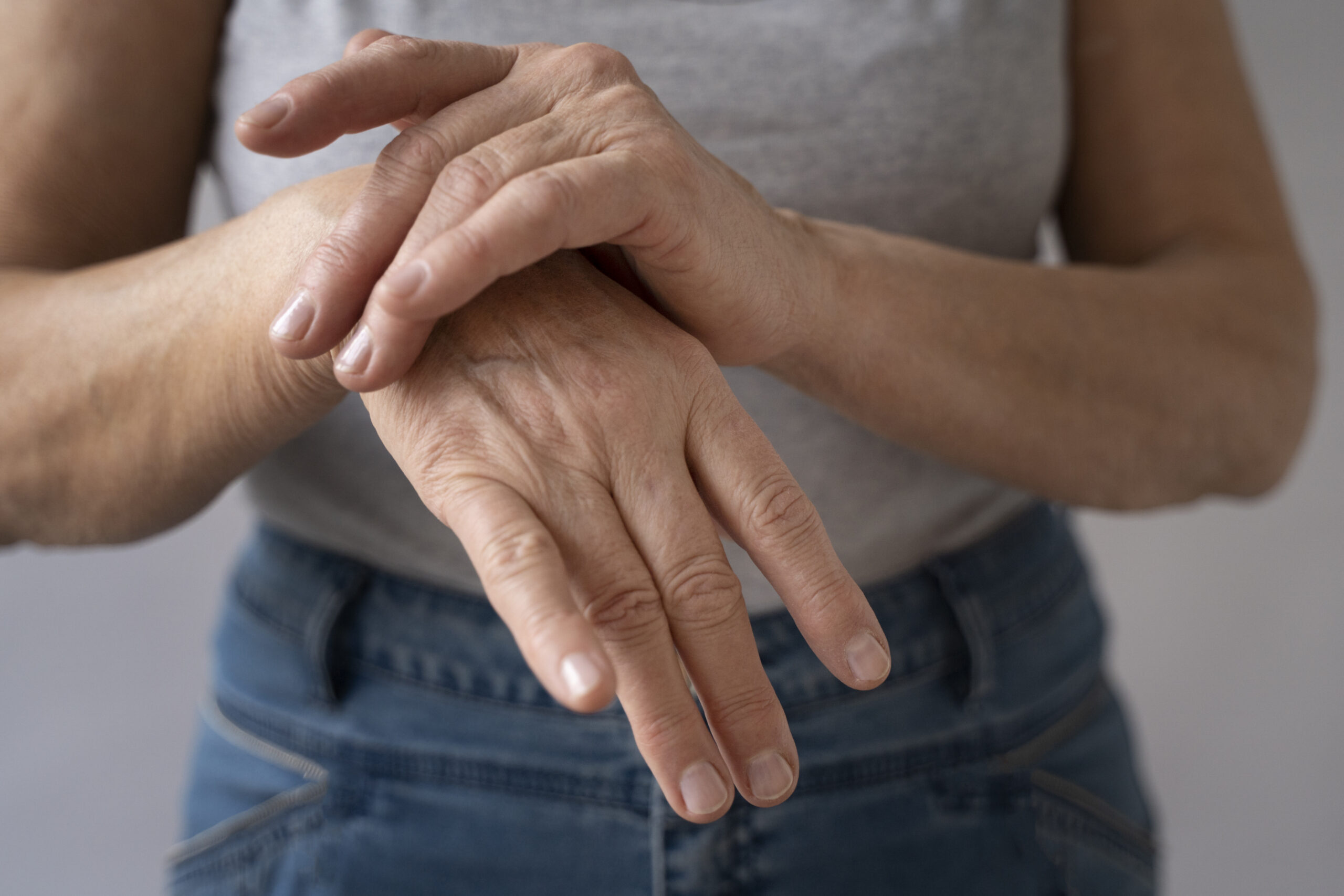
Autoimmune disorders are among the most complex medical conditions to diagnose and manage because they often affect multiple systems in the body. These conditions occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation, pain, fatigue, and progressive damage if left untreated. Managing Autoimmune Disease requires a deep understanding of immune system behavior, disease patterns, and long-term care strategies, which is why specialized medical expertise plays such a critical role from the very beginning of diagnosis.
Why Specialized Rheumatology Care Is Essential
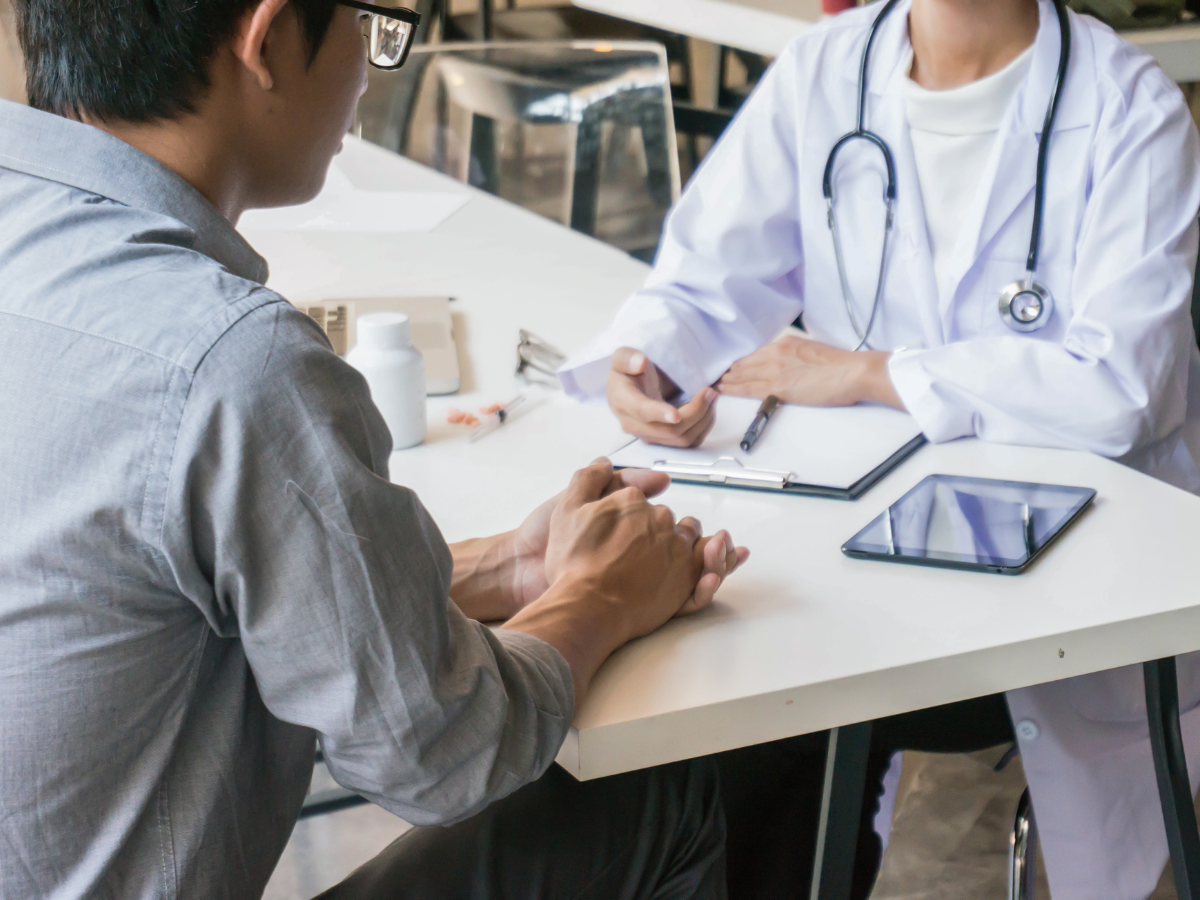
Rheumatologists are uniquely trained to recognize subtle symptoms that may be overlooked in general medical evaluations. Many autoimmune conditions present with overlapping signs such as joint stiffness, muscle pain, swelling, and unexplained fatigue. A rheumatologist’s specialized training allows them to identify underlying autoimmune activity early, reducing delays in treatment and helping prevent irreversible joint and organ damage. Their role goes far beyond symptom control and focuses on comprehensive disease management.
Accurate Diagnosis Through Advanced Evaluation
One of the most important roles of a rheumatologist is achieving an accurate diagnosis. Autoimmune conditions often mimic other illnesses, making diagnosis challenging without expert evaluation. Rheumatologists use detailed patient histories, physical examinations, laboratory testing, and imaging studies to differentiate between conditions and determine disease severity. This precision ensures patients receive the most appropriate and effective treatment plan rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.
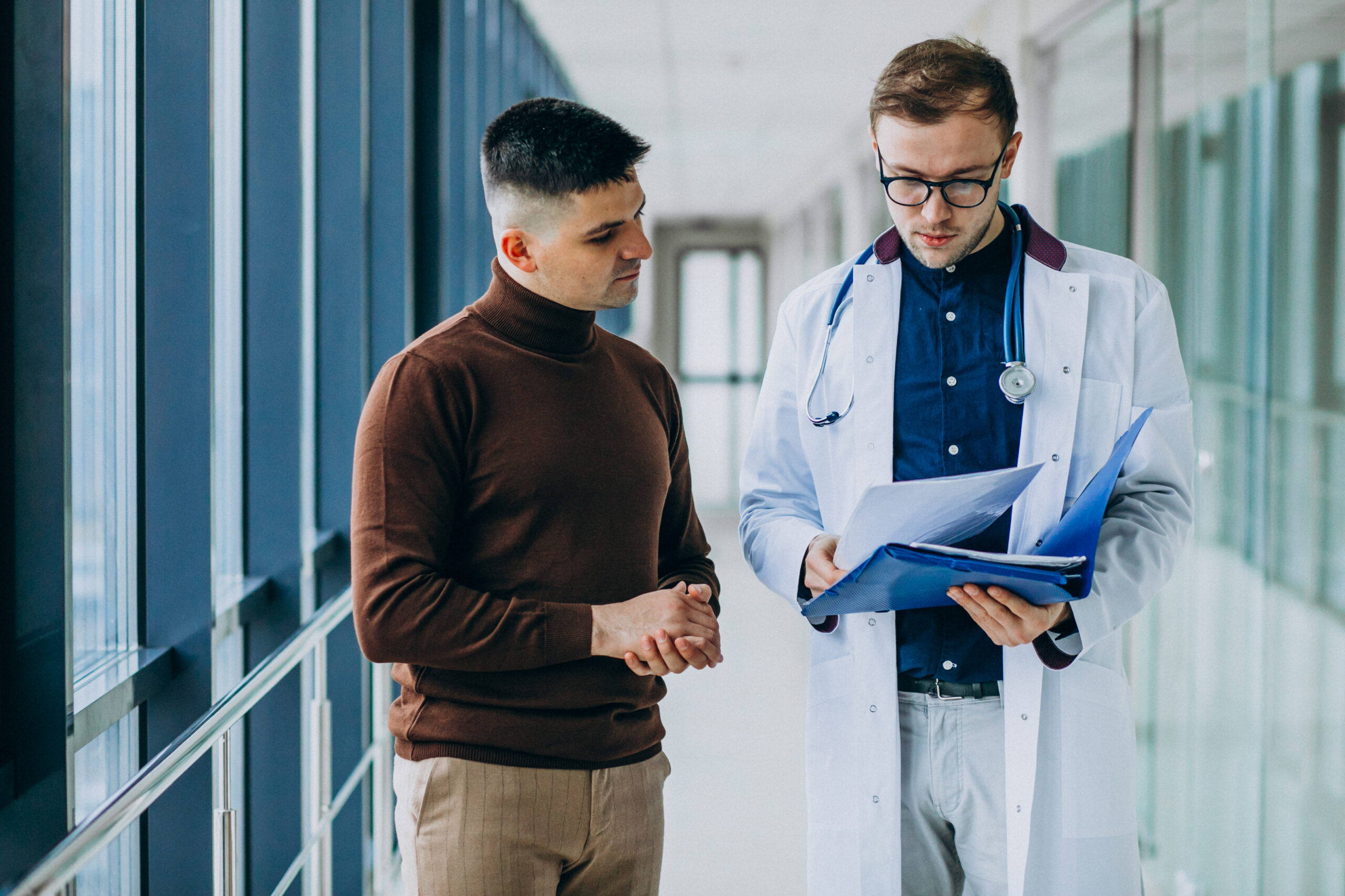
Creating Personalized Treatment Plans
Autoimmune conditions affect every patient differently, even when the diagnosis is the same. Rheumatologists develop personalized treatment plans based on disease activity, lifestyle factors, and individual health needs. Treatment strategies may evolve over time, requiring regular monitoring and adjustment. This individualized care approach helps control inflammation, minimize flare-ups, and improve overall quality of life while reducing the risk of long-term complications.
Managing Advanced and Complex Therapies
Modern autoimmune care often involves advanced therapies that require expert oversight. Rheumatologists are experienced in managing biologic medications, immunosuppressive therapies, and infusion treatments that target specific immune pathways. These therapies can significantly reduce disease progression when administered correctly. Ongoing monitoring by a specialist ensures treatments remain safe, effective, and aligned with the patient’s changing condition.
Preventing Disease Progression and Complications
Without proper management, autoimmune conditions can lead to permanent joint damage, organ involvement, and disability. Rheumatologists play a proactive role in preventing disease progression by addressing inflammation early and consistently. Through regular follow-ups and treatment optimization, they help reduce complications, preserve mobility, and support long-term health outcomes for patients living with chronic autoimmune disorders.
Supporting Long-Term Disease Management
Autoimmune conditions are typically lifelong, requiring continuous care rather than short-term treatment. Rheumatologists guide patients through long-term disease management by monitoring symptoms, adjusting therapies, and addressing new health concerns as they arise. This continuity of care helps patients better understand their condition and remain actively involved in managing their health over time.
Improving Quality of Life for Patients
Beyond medical treatment, rheumatologists focus on improving daily functioning and overall well-being. By reducing pain, controlling inflammation, and limiting flare-ups, patients are better able to maintain independence and engage in everyday activities. Education, reassurance, and consistent medical support play an important role in helping patients feel empowered and confident in managing their condition.
Conclusion
The management of complex autoimmune conditions requires specialized knowledge, ongoing evaluation, and personalized care strategies. Rheumatologists serve as essential partners in guiding patients through diagnosis, treatment, and long-term disease control. At VIP Rheumatology, expert care is focused on addressing Autoimmune Disease with precision, compassion, and advanced treatment approaches that support lasting health and improved quality of life.